Calcium is one of the most essential minerals for life. As per research published on PubMed, it is the most abundant mineral in the body, with about 99% of the body’s calcium stored in the bones and teeth.
That is why calcium is crucial for maintaining strong bones and teeth and for various other functions in the body, such as muscle function, nerve signaling, and hormone secretion.
A person is observed to have calcium deficiency if there are insufficient levels of calcium in the blood. This condition is also known as hypocalcemia. In this condition, the body may draw calcium from the bones to maintain normal blood levels. Over time, this can weaken the bones and lead to bone fractures or other medical conditions like osteoporosis.
It is observed that calcium deficiency is a common nutritional issue, especially among certain groups like postmenopausal women, the elderly, and those individuals with lactose intolerance or having certain medical conditions that affect calcium absorption.
Also, calcium absorption can be influenced by other nutrients, mainly vitamin D and magnesium. Ensuring an adequate intake of these nutrients is important for maintaining calcium balance in the body, as preventing calcium deficiency is crucial for overall health and well-being.
Treatment of calcium deficiency usually includes increasing dietary intake of calcium-rich foods, such as dairy products, leafy green vegetables, and fortified foods. Calcium supplements are also recommended for severe calcium deficiency.
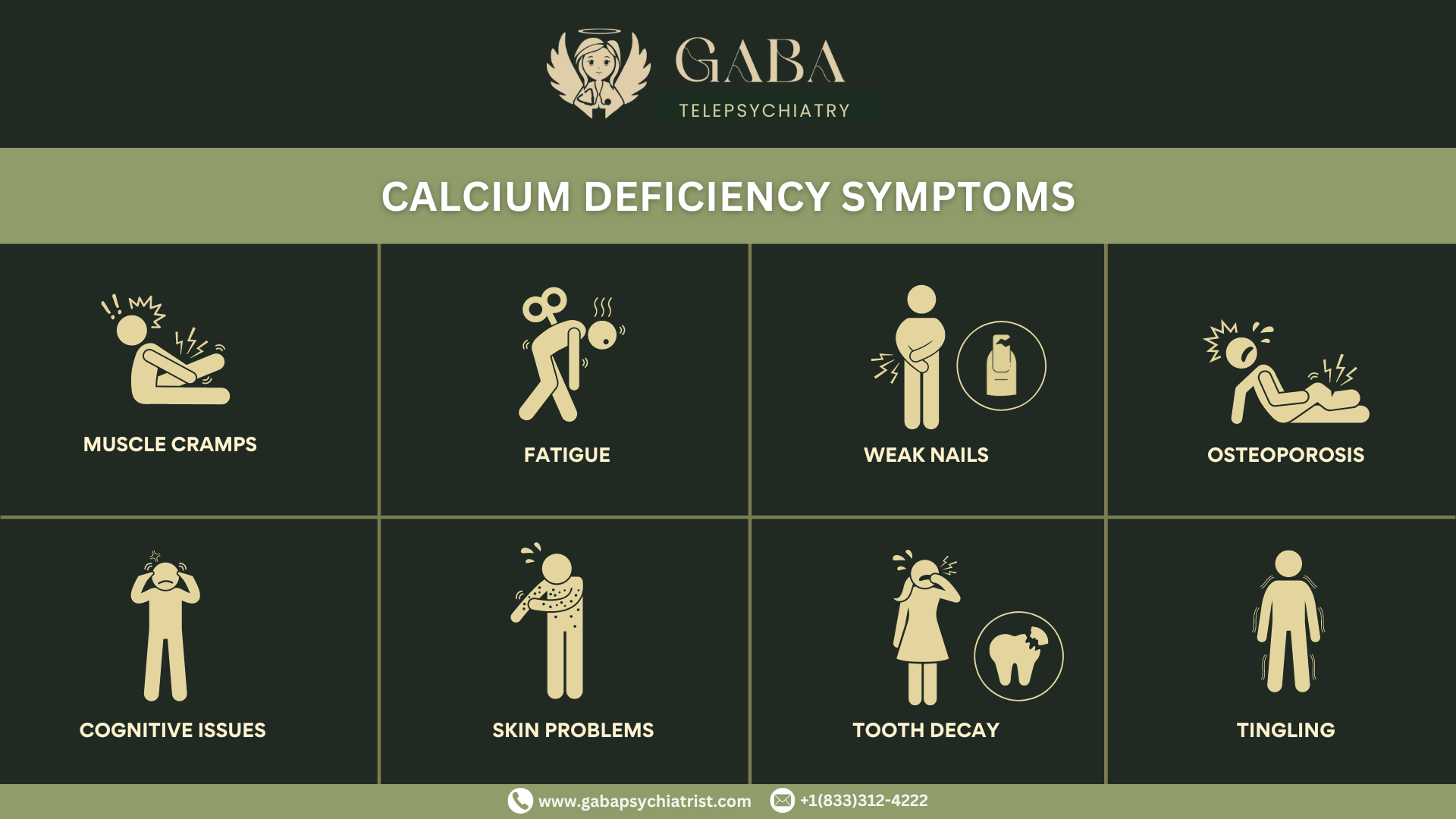
Calcium Deficiency Symptoms
Calcium deficiency can lead to various physical symptoms, particularly when it becomes severe. Some are mentioned below:
- Muscle cramps
- Tingling
- Weak nails
- Osteoporosis
- Tooth decay
- Fatigue
- Skin problems
- Cognitive issues
Calcium Deficiency and Muscle Cramps
Muscle cramps are sudden, involuntary contractions or spasms in one or more muscles. They can occur in various body parts, such as the legs, feet, hands, or abdomen, and can range from mild to extremely painful. Cramps can last anywhere from a few seconds to several minutes. It can occur not only during physical activity but also during rest or sleep.
Muscle cramps can have various causes, but calcium deficiency is one of the major potential factors. It has been found that calcium is an essential mineral that plays a key role in muscle function. When a muscle contracts, calcium ions are released from storage sites within the muscle cells, which allows the muscle fibers to slide past each other and generate force.
Calcium deficiency can disrupt this process, which leads to muscle cramps. It was concluded that without enough calcium, the muscle fibers may not be able to fully relax after contraction, resulting in prolonged or involuntary muscle contractions characteristic of cramps.
Calcium Deficiency and Tingling
Tingling or numbness are abnormal sensations often described as pins-and-needles feelings or reduced sensitivity in a specific body area. Numbness is a complete or partial loss of feeling or sensation in any area of your body. Most of the time, numbness isn’t serious, but severe cases can lead to complications such as not being able to feel pain.
Calcium deficiency is not directly associated with tingling or numbness. However, severe calcium deficiency, known as hypocalcemia, can lead to numbness or tingling in the fingers and toes. Calcium plays a crucial role in nerve function. Low calcium levels can lead to increased nerve excitability, potentially causing tingling sensations or numbness, particularly in the extremities like the fingers and toes.
Calcium Deficiency and Weak Nails
Weak and brittle nails are nails that are easily broken, cracked, or split. This condition can result from various factors, including nutritional deficiencies (such as calcium), excessive dryness due to low humidity, or frequent exposure to water and chemicals. Also, regular contact with harsh chemicals like nail polish remover or cleaning products can harm nails.
It has been observed that calcium is essential for maintaining strong and healthy nails. Calcium plays a crucial role in the strength and structure of nails, contributing to the integrity of the nail plate and preventing brittleness. Calcium also promotes and regulates cell growth and differentiation in the nail matrix, which is important for continuous nail renewal. In addition to this, calcium helps in maintaining the proper moisture balance in the nails, which prevents dryness and further enhances nail strength. However, calcium deficiency can affect nail health and appearance.
Calcium Deficiency and Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a medical condition characterized by weakened bones that are more susceptible to fractures and breaks. This condition is caused when the body loses too much bone, makes too little bone, or both. As a result, bones become weak, porous, and brittle, leading to a higher risk of fractures, particularly in the hip, spine, and wrist. Osteoporosis is often referred to as a “silent disease” because it progresses without symptoms until a fracture occurs.
Calcium supports bone health and strength; therefore, playing a crucial role in preventing osteoporosis. However, its deficiency can significantly impact bones and contribute to osteoporosis. When calcium levels are low, the body may draw calcium from bones, which leads to reduced bone density and an increased risk of fractures.
Calcium Deficiency and Tooth Decay
Tooth decay, also known as dental caries or cavities, is a common oral health problem that occurs when bacteria in the mouth produce acids that erode the tooth enamel. This erosion tends to form small holes or cavities in the teeth. Tooth decay can cause pain and sensitivity, and eventually, if left untreated, it can lead to more serious dental problems such as infections or tooth loss.
Calcium is a key component of tooth enamel, the hard outer layer of the tooth that protects it from decay and helps in maintaining healthy teeth. When the body lacks sufficient calcium, it may not be able to maintain the health and integrity of the enamel, making it more susceptible to acid erosion and decay. Therefore, calcium deficiency can affect the overall health, and strength of the teeth and gums, potentially leading to other oral health issues that contribute to tooth decay.
Calcium Deficiency and Fatigue
In addition to all these, chronic fatigue, which lasts for an extended period and does not go away with mere rest, can significantly impact a person’s quality of life. It may indicate an underlying health issue that requires medical attention.
Calcium deficiency can contribute to fatigue through its effects on muscle function and energy production. It has been observed that calcium plays a crucial role in muscle contraction, including the muscles involved in maintaining posture and movement. However, when calcium levels are low, muscle function can be impaired, which leads to muscle weakness and fatigue.
In addition to this, calcium is involved in cellular energy production. Therefore, adequate calcium levels are necessary for the proper functioning of enzymes involved in energy metabolism. Its deficiency can disrupt these processes, potentially leading to decreased energy levels and feelings of fatigue.
Calcium Deficiency and Skin Problems
Skin problems can be referred to as conditions or issues that affect the appearance, texture, or function of the skin. These issues can range from mild to severe cases and can manifest in various ways. Commonly caused skin problems include acne, eczema, psoriasis, rosacea, dermatitis, hives, skin infections, skin cancer, hyperpigmentation, and dry skin.
Calcium is found to be very essential for various cellular functions, including skin cell turnover and regeneration. When calcium levels are low, it can affect the skin’s ability to maintain its normal function and health, which leads to issues such as dryness, itching, or rashes.
In addition to this, severe calcium deficiency (hypocalcemia) can cause symptoms such as muscle cramps and spasms, which can indirectly impact the skin if these symptoms interfere with regular movement and skin care routines.
Calcium Deficiency and Cognitive issues
Cognitive issues mainly comprise a range of difficulties related to cognitive function, which includes thinking, learning, memory, and decision-making. These issues can vary in severity and duration, and can also impact various aspects of daily life.
Common cognitive issues include memory problems, attention and concentration difficulties, language and communication problems, executive function impairments, processing speed reduction, and cognitive fatigue.
Calcium is crucial for proper nerve function and neurotransmitter release, which are essential for cognitive processes such as learning and memory, but severe calcium deficiency, known as hypocalcemia, leads to neurological symptoms such as confusion, memory loss, and seizures, which affect cognitive functions.
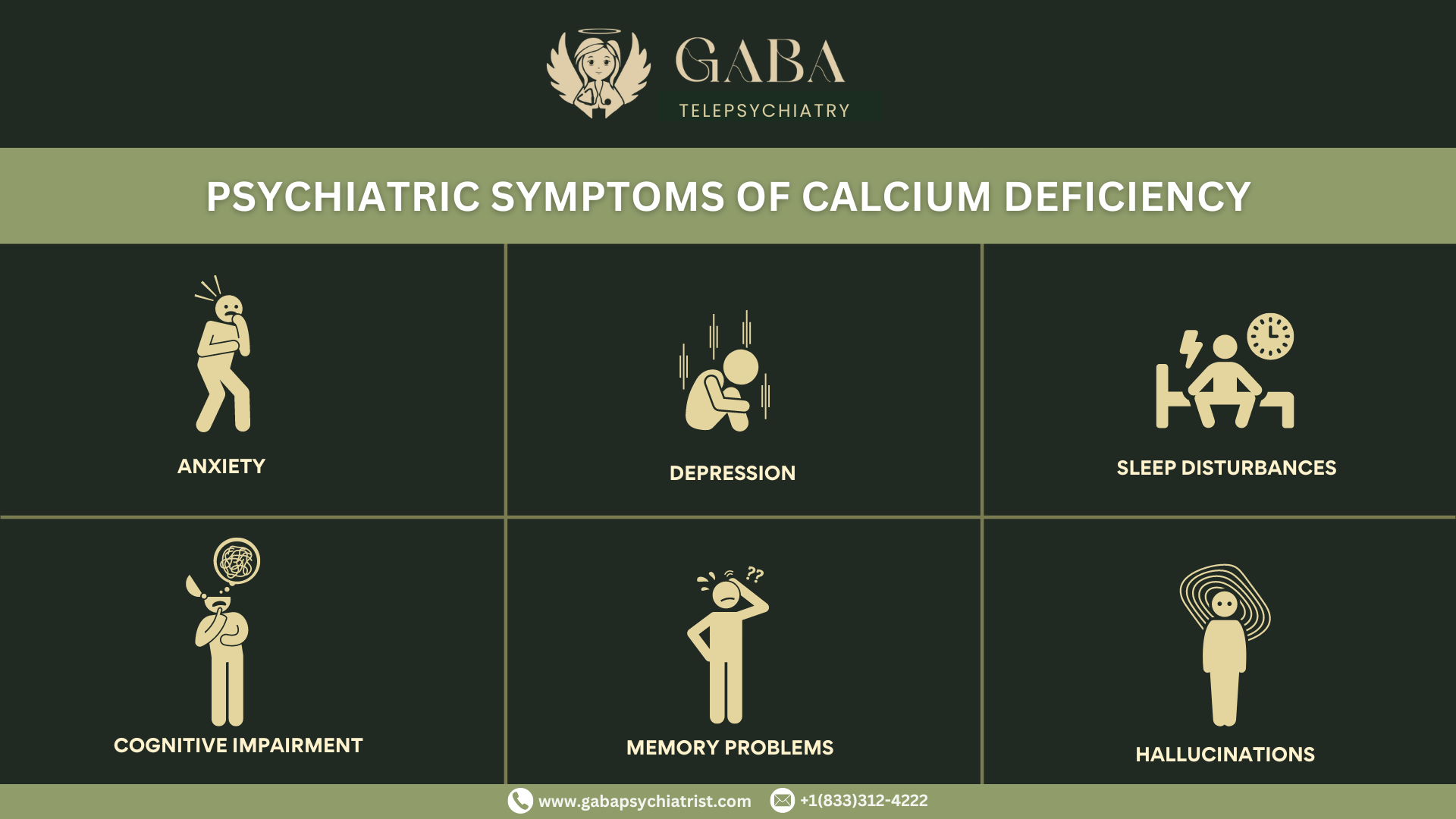
Psychiatric Symptoms of Calcium Deficiency
Calcium deficiency can potentially lead to psychiatric symptoms, but severe calcium deficiency, known as hypocalcemia, can affect brain function and neurotransmitter activity, which may contribute to psychiatric symptoms. Some are mentioned below:
- Depression
- Anxiety
- Sleep disturbances
- Cognitive impairment
- Memory problems
- Hallucinations
Calcium Deficiency and Depression
Depression is a type of serious mood disorder that can negatively affect how you feel, think, and react. It causes feelings of persistent sadness, a loss of interest in once enjoyable activities, and many physical and emotional problems. Depression may interfere with your ability to properly function at work, school, or in relationships.
Researchers have observed that calcium plays a role in the release of neurotransmitters such as serotonin, which is crucial for mood regulation. Low serotonin levels have been linked to depression, and disruptions in calcium signaling could potentially affect serotonin levels.
In addition to this, calcium is also involved in the regulation of hormones such as parathyroid hormone (PTH) and calcitriol (the active form of vitamin D), which can impact mood and mental health. Calcium deficiency can affect these hormonal pathways and cause mood disorders like depression.
Calcium Deficiency and Anxiety
Anxiety is often described as feelings of worry, nervousness, or unease about something with an uncertain outcome, and sometimes feelings of fear and dread don’t go away or get worse over time.
It can be a response to stress or a perceived threat and is often accompanied by physical sensations such as an increased heart rate, sweating, trembling, or feelings of tension.
It has been observed that calcium plays a role in the release of neurotransmitters such as gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which has calming effects on the brain. And low calcium levels in the body could potentially affect GABA activity, leading to increased anxiety.
Other than this, calcium is essential for muscle contraction and relaxation, including the muscles involved in breathing. However, calcium deficiency could potentially lead to muscle tension and respiratory changes, which are associated with anxiety.
Calcium Deficiency and Sleep Disturbances
Sleep disturbances are disruptions in the normal sleep pattern that can affect the quality and duration of sleep. These disturbances can manifest in various ways, including difficulty falling asleep, frequent awakenings during the night, waking up too early and being unable to fall back asleep, or non-restorative sleep.
Chronic sleep disturbances can have a significant impact on overall health and well-being, leading to daytime fatigue, irritability, difficulty concentrating, and an increased risk of developing other health problems.
Calcium plays a role in regulating hormones such as melatonin, also known as the “sleep hormone” because it helps regulate the sleep-wake cycle. Disruptions in calcium balance could potentially affect melatonin production and disrupt the sleep-wake cycle. Additionally, calcium is essential for muscle contraction and relaxation.
Adequate calcium levels help muscles relax properly, which is important for falling asleep and staying asleep. Calcium deficiency could potentially lead to muscle cramps or spasms, which may disrupt sleep.
Calcium Deficiency and Cognitive Impairment
Cognitive impairment refers to a decline in cognitive function that affects a person’s ability to think, learn, remember, and make decisions. It can range from mild to severe and can be temporary or progressive. Early detection and management of cognitive impairment are crucial because they help maintain quality of life and independence.
Calcium plays a crucial role in releasing the acetylcholine neurotransmitter, which is important for memory and learning. Low calcium levels could potentially lead to decreased acetylcholine activity, which may contribute to cognitive impairment.
Calcium ions are also involved in neuronal excitability, which is found to be important for proper brain function. Changes in calcium levels could potentially affect neuronal activity and contribute to cognitive impairment.
Calcium Deficiency and Memory Problems
Memory problems refer to difficulties in remembering information, events, or experiences, and all these problems can manifest in various ways, including forgetting recent conversations or events, having trouble recalling important details or experiencing difficulty learning new information. Memory problems may be temporary and reversible, but in some other cases, they may be a sign of a more serious underlying condition.
Calcium is found to be very important for maintaining the structure and function of brain cells. Low calcium levels could potentially lead to changes in brain structure or function that contribute to memory problems. In addition to this, Calcium deficiency has been associated with increased oxidative stress and inflammation, which increases the chances of the development of memory problems.
Calcium Deficiency and Hallucinations
Hallucinations are sensory experiences that occur in the absence of external stimuli. These experiences can involve seeing, hearing, smelling, tasting, or feeling things that are not real. Hallucinations can be vivid and seem very real to the person experiencing them, and they can also cause fear in the person.
It has been concluded from the above section that calcium is involved in neurotransmitter release, including dopamine, which plays a role in perception and cognition.
However, calcium deficiency could potentially lead to altered dopamine activity, which may contribute to hallucinations. In addition to this, calcium deficiency has a significant impact on neuronal activity and can also cause electrolyte imbalances, all of which can contribute to hallucinations.
These symptoms have a significant impact on the overall well-being of a person. Treatment for symptoms of calcium deficiency involves addressing the underlying deficiency through dietary changes or supplements. So, It is always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
To learn more about our services and seek help for nutritional deficiencies, visit www.gabapsychiatrist.com.